The Array object, as with arrays in other programming languages, enables storing a collection of multiple items under a single variable name, and has members for performing common array operations.
Array()
Accepts 1 integer argument and returns an array with those elements.
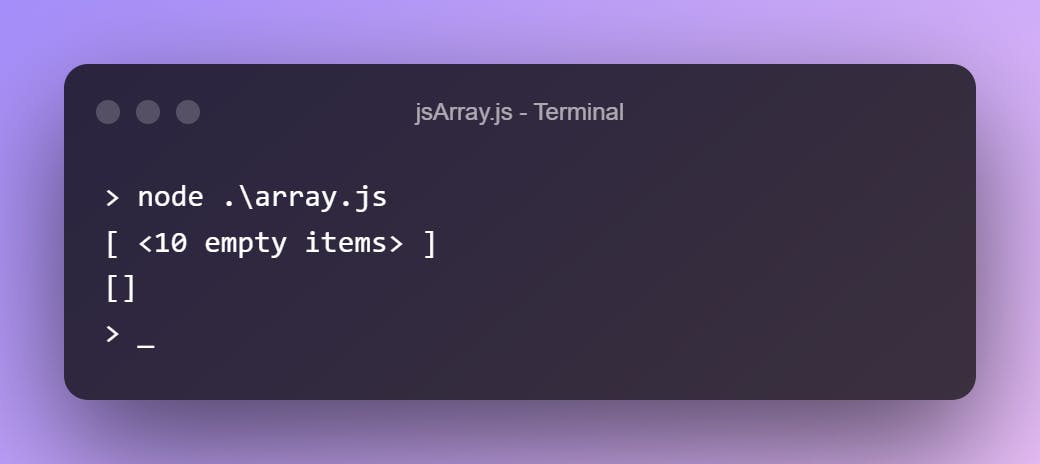
Array(10)
Array()
.from()
This method is used to create an array. It accepts two arguments, the first one accepts an array or some iterable object.
Array.from("Any String")

.isArray()
This method accepts one argument and returns` if it's an array.
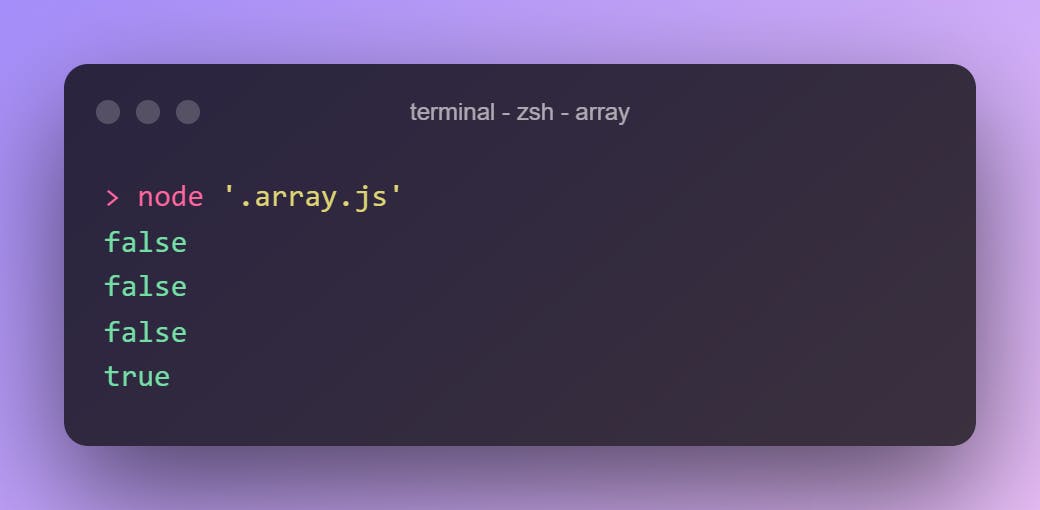
Array.isArray("")
Array.isArray()
Array.isArray(42)
Array.isArray([])
.at()
Returns the element of the array of the given position.
You can use negative numbers instead of doing array[array.length-1].
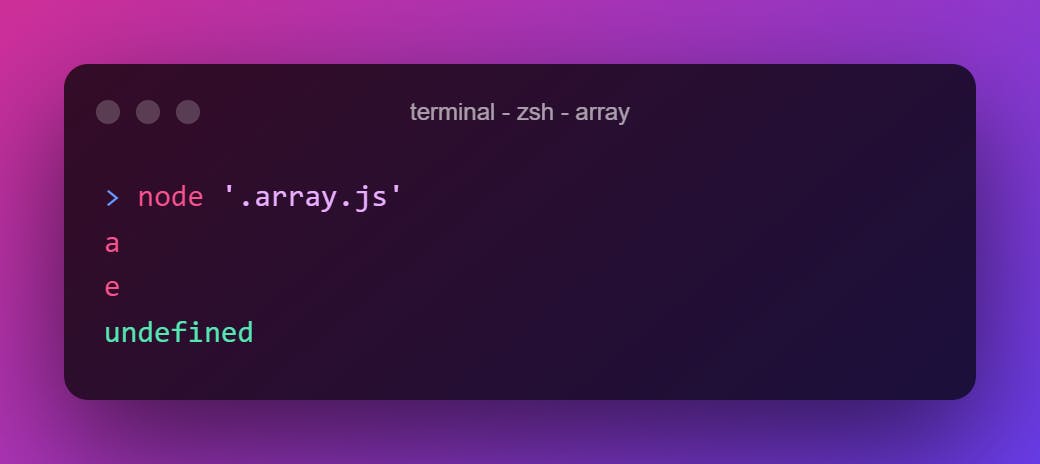
["a","b","c","d","e"].at(0)
["a","b","c","d","e"].at(-1)
["a","b","c","d","e"].at(42)
.concat()
Merges all the arguments to one array.
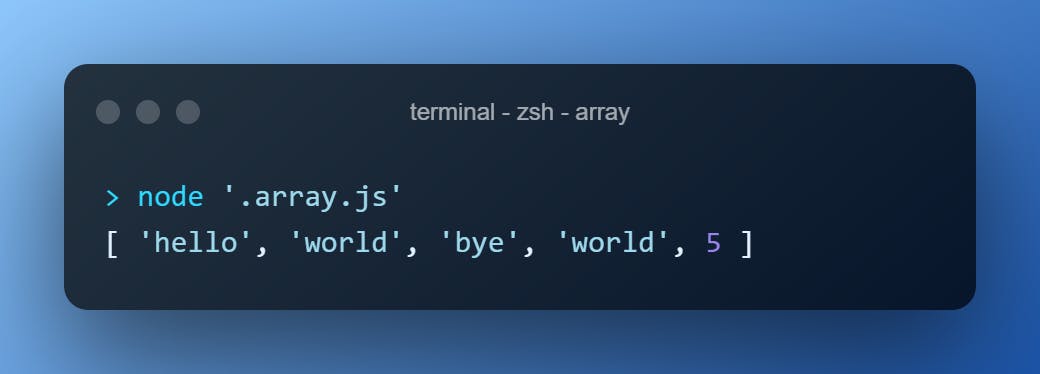
["hello"].concat("world", "bye", "world", [5])
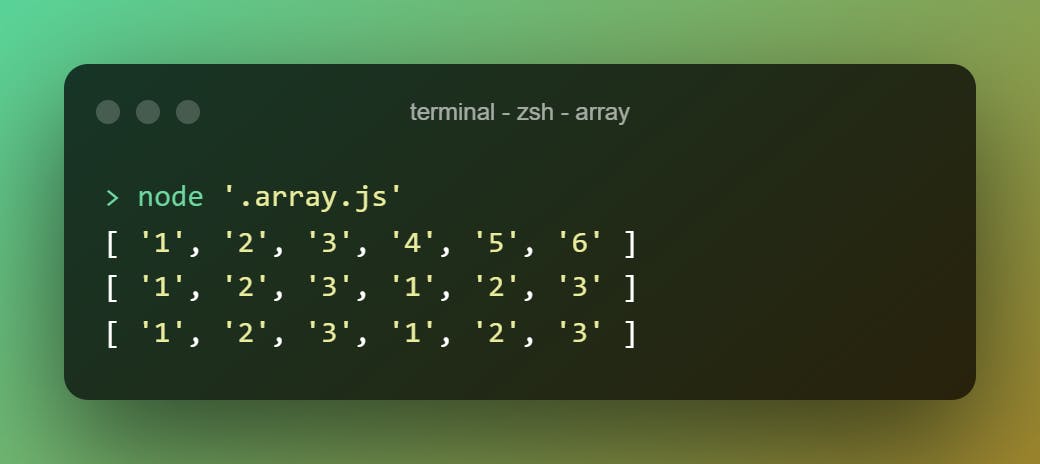
.copyWithin()
Copies the array within a range. Accepts 3 arguments.
["1","2","3","4","5","6"].copyWithin(0)
["1","2","3","4","5","6"].copyWithin(3, 0)
["1","2","3","4","5","6"].copyWithin(3, 0, 4)
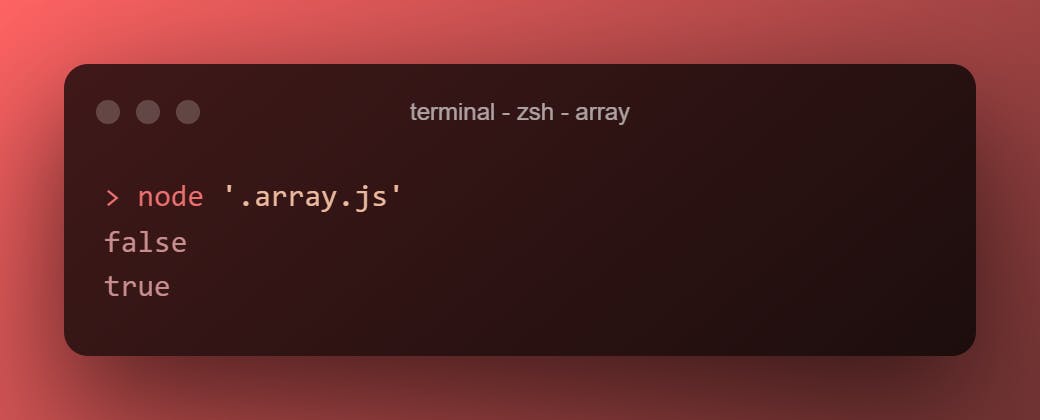
.every()
Accepts a test function and returns a boolean if all the elements of the array pass the test.
["gonna", "give", "you"].every((element) => element.startsWith("g"))
["apple", "android", "aluminium"].every((element) => element.startsWith("a"))
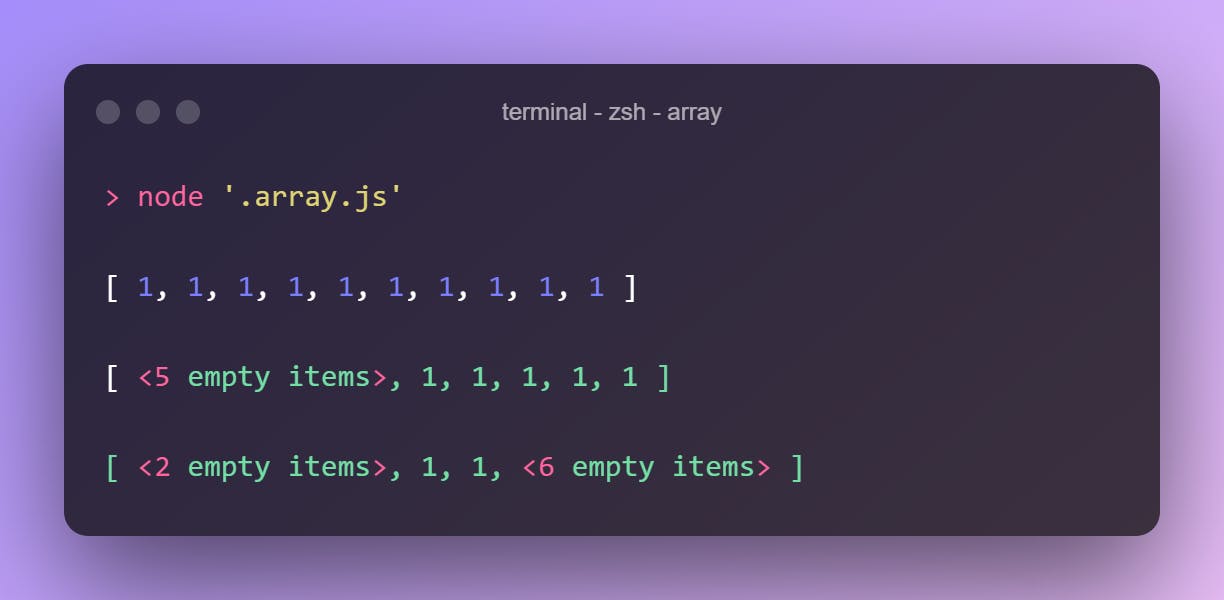
.fill()
Fills the array with a given value. Accepts 3 arguments.
1st argument is the value we need to fill.
The 2nd argument is the starting index.
The last argument is the ending index.
(The last two parameters are optional.)
.filter()
Accepts a test function to loop each array element and remove that element if failed the test.
["eating", "sleeping", "coding", "playing"].filter(element => element != "sleeping")
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10].filter(element => element % 2)

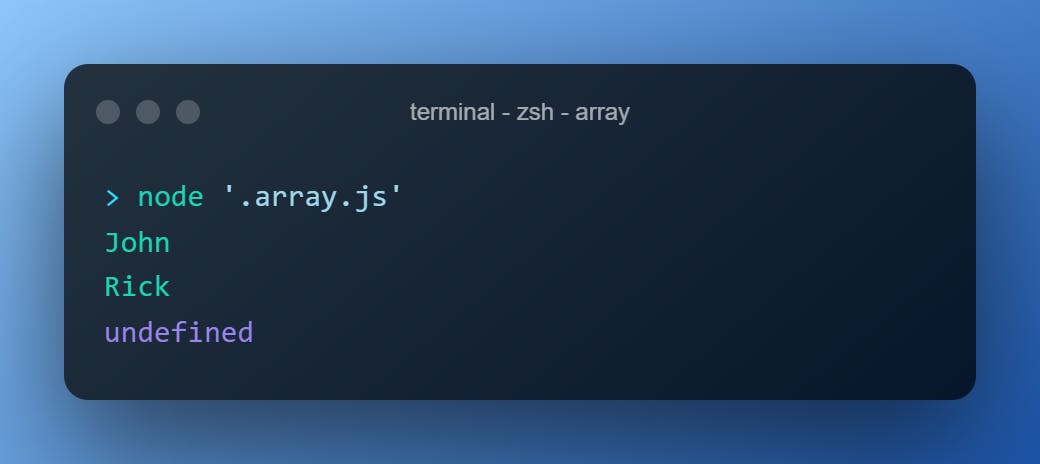
.find()
This accepts a test function and returns the element that the test function passed.
const people = ["John", "Anna", "Peter", "Rick", "Elon"]
const search = name => people.find(element => element.startsWith(name))
console.log( search("Jo") );
console.log( search("Rick") );
console.log( search("Ben") );
.findIndex()
This returns the position of the element in the array.
const people = ["John", "Anna", "Peter", "Rick", "Elon"]
const search = name => people.findIndex(element => element.startsWith(name))
console.log(search("Jo"));
console.log(search("Rick"));
console.log(search("Ben"));
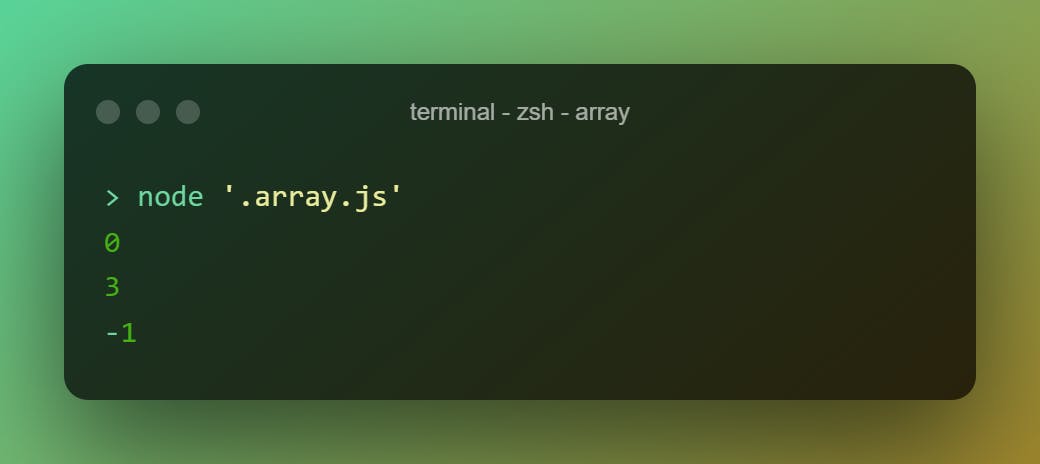
.flat()
Flats the array to a given depth. The depth will be one if no value.
[1, [2, [3, [4]]], 5].flat()
[1, [2, [3, [4]]], 5].flat(2)
[1, [2, [3, [4]]], 5].flat(3)
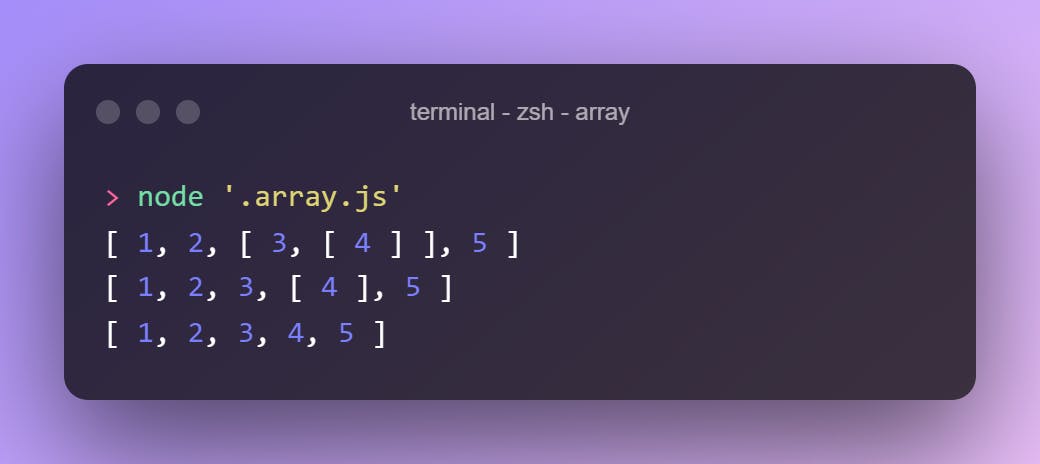
.forEach()
Accepts an argument that will call for each element of the array
["one","two","three","four"].forEach(alert)
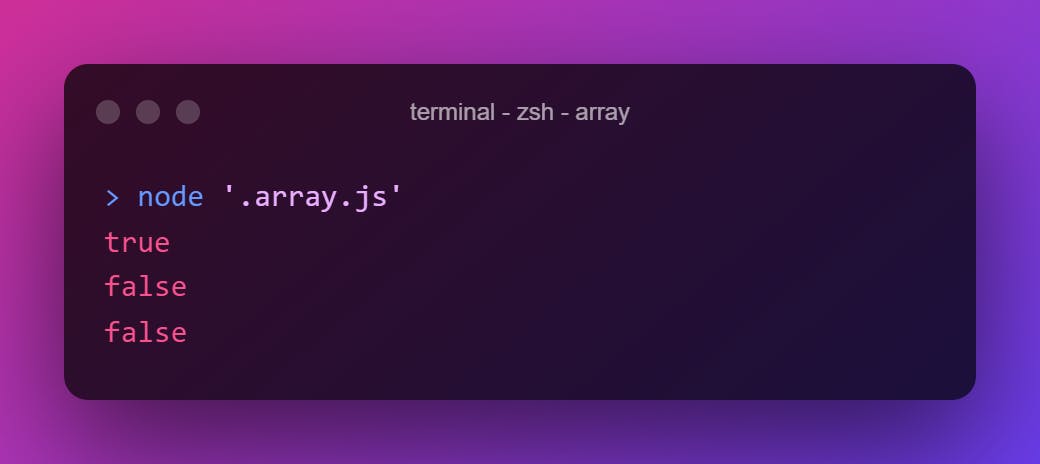
.includes()
Returns if the array contain the given value. Also, this is case-sensitive.
["ant","bat","cat","rat","man"].includes("man")
["ant","bat","cat","rat","man"].includes("Man")
["ant","bat","cat","rat","man"].includes("dog")
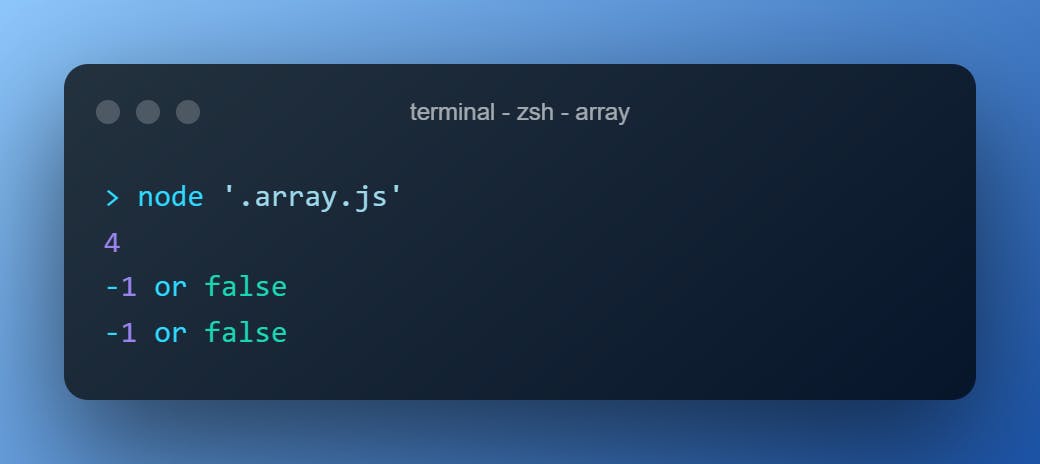
.indexOf()
Returns the least index of an element of the array (if found) after searching the value.
Returns -1 if not found.
The 2nd argument specifies the position to start the search.
["ant","bat","cat","rat","man"].indexOf("man")
["ant","bat","cat","rat","man"].includes("Man")
["ant", "bat", "cat", "rat", "man"].includes("ant", 2)
.join()
Joins all the array elements into a string with a separator (if given).
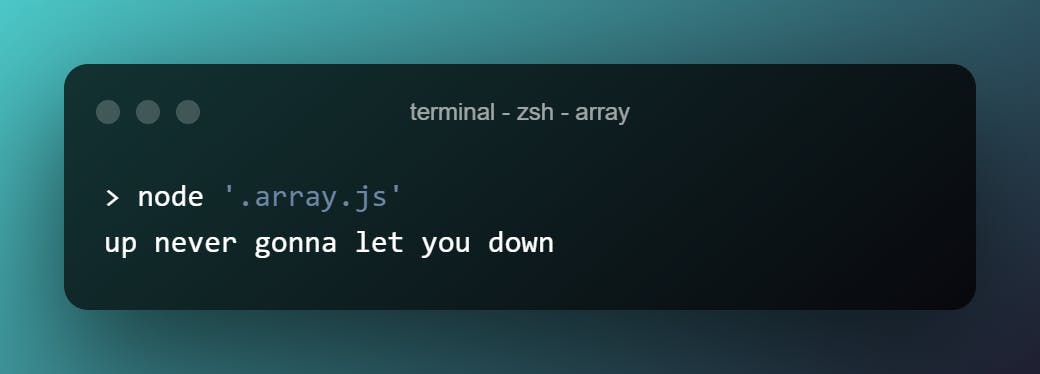
["up", "never", "gonna", "let", "you", "down"].join` `
.lastIndexOf()
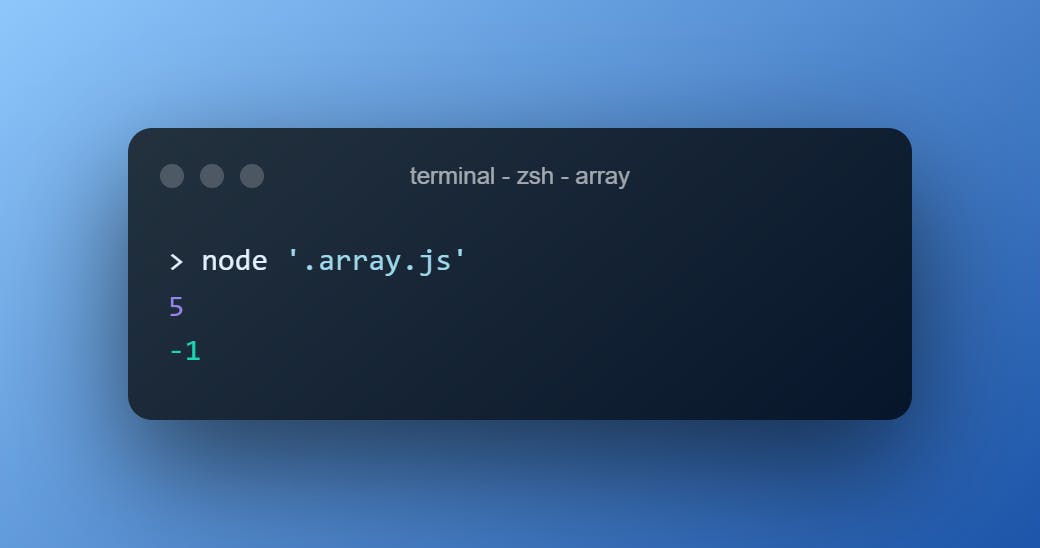
Returns the largest index of an element of the array after searching the value
["a", "aaa", "aaa", "aa", "a", "aaa"].lastIndexOf("aaa")
["a", "aaa", "aaa", "aa", "a", "aaa"].lastIndexOf("b")
.map()
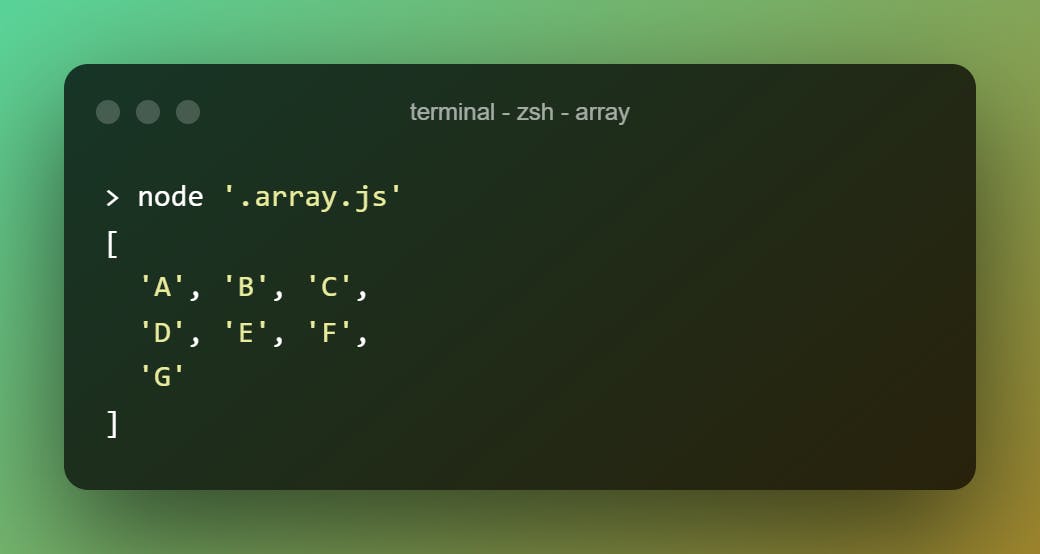
Loops for each element of the array and executes the given function and change the value to the output of the function.
["a","b","c","d","e","f","g"].map(e=>e.toUpperCase())
.pop()
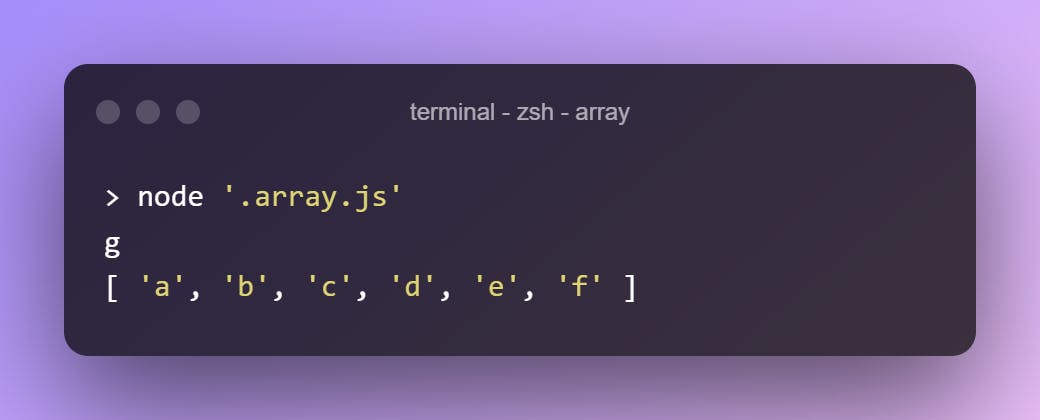
Removes the last element of the array and returns it.
let arr = ["a","b","c","d","e","f","g"]
console.log(arr.pop())
console.log(arr)
.shift()
Removes the first element and return that element.
let arr = ["a","b","c","d","e","f","g"]
console.log(arr.shift())
console.log(arr)

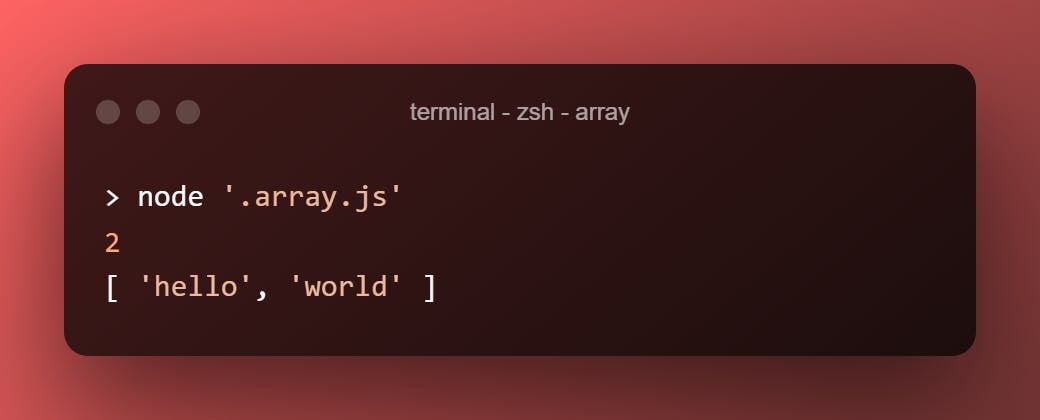
.push()
Push the given value to the array. Then, return the new length of the array.
let h = ["hello"]
console.log(h.push("world"))
console.log(h)
.unshift()
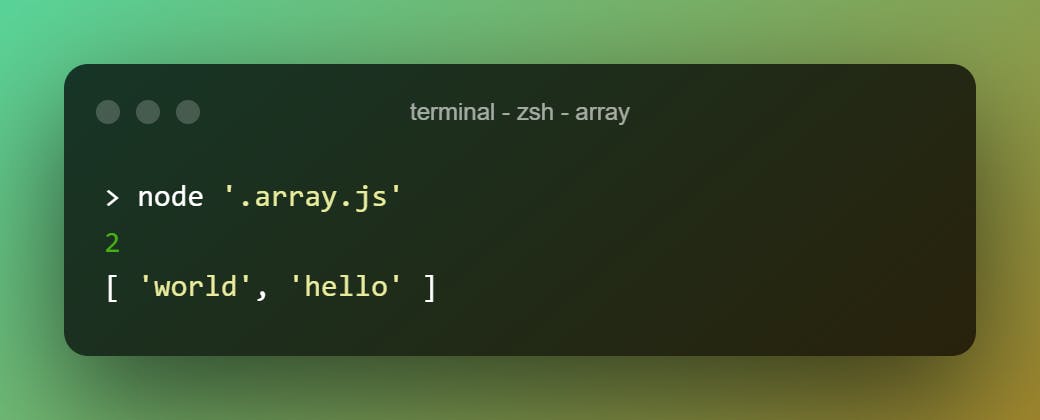
Does the same as .push but adds the elements to the first ( at 0th index).
let h = ["hello"]
console.log(h.unshift("world"))
console.log(h)
.reduce()
Accepts a reducer function as the first argument and executes it.
The second arguments show the initial value, and it's optional.
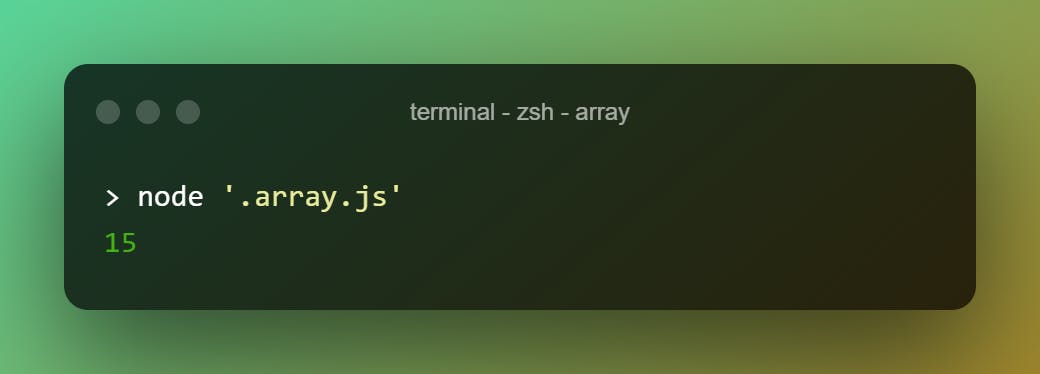
To calculate the sum of an array, we can do this.
let tot = 0
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
array.forEach(e => (tot += e))
console.log(tot)
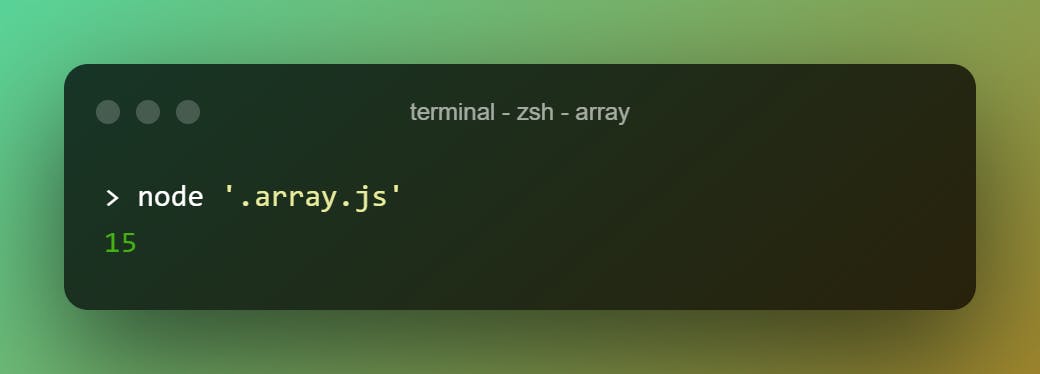
There is no problem of doing that, but we can use .reduce() to that.
const dummy = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].reduce((previous, current) => previous + current, 0)
console.log(dummy)
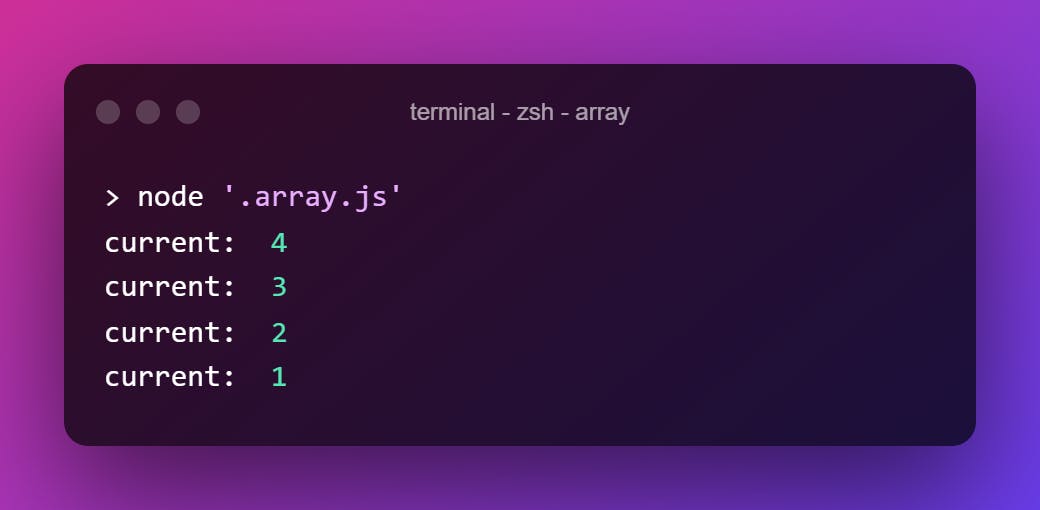
.reduceRight()
Same as .reduce() but executes from the last to start of the array. If we do a quick test, we can see this.
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].reduceRight((previous, current) => {
console.log("current: ", current)
return previous + current
})
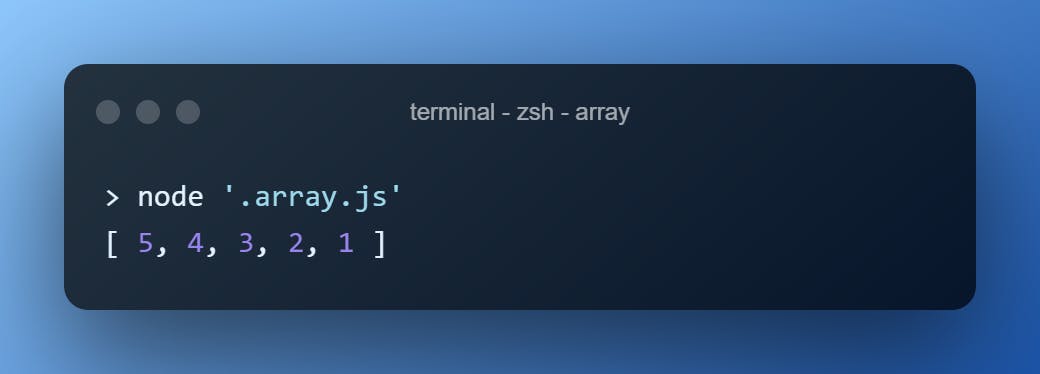
.reverse()
Reverse the array!
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].reverse()
.slice()
It's like cutting an array.
It accepts 2 arguments. The start index and the end.
["head","neck","body","feet"].slice()
["head","neck","body","feet"].slice(1)
["head", "neck", "body", "feet"].slice(1, 3)

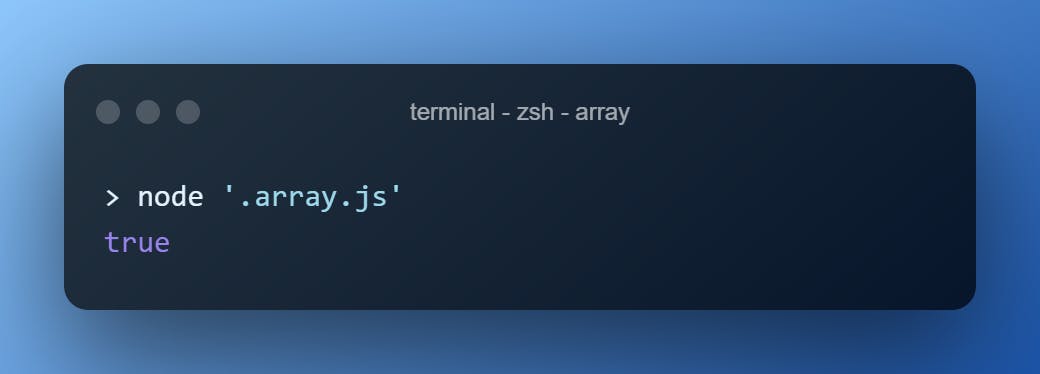
.some()
Accepts a function that tests and returns if one or more elements of the array passes that.
const ages = [42, 69, 1, 25, 34, 14]
ages.some(age => age > 60)
.sort()
Sorts an array and returns the sorted array. You can also use your own sorting function.
[1, 2, 4, 8, 4, 2, 1, 6, 8, 4, 2, 7, 56, 2, 9, 5, 52, 1].sort()
